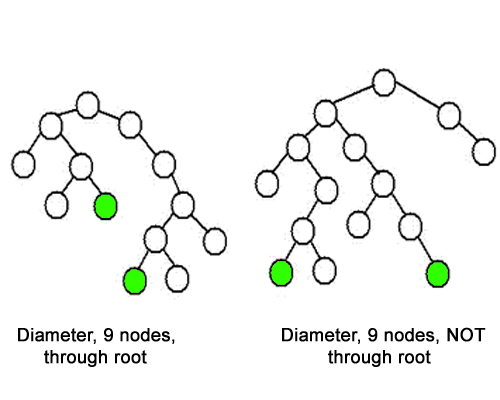
The diameter of a tree (sometimes called the width) is the number of nodes on the longest path between two end nodes. The diagram below shows two trees each with diameter nine, the leaves that form the ends of the longest path are shaded (note that there is more than one path in each tree of length nine, but no path longer than nine nodes).
Example 1:
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input:
10
/ \
20 30
/ \
40 60
Output: 4
Your Task:
You need to complete the function diameter() that takes root as parameter and returns the diameter.
Expected Time Complexity: O(N).
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(Height of the Tree).
Constraints:
1 <= Number of nodes <= 10000
1 <= Data of a node <= 1000