|
| 1 | +### 题目描述 |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +这是 LeetCode 上的 **[2876. 有向图访问计数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-visited-nodes-in-a-directed-graph/solutions/2512278/gong-shui-san-xie-sha-shi-nei-xiang-wai-d3lm9/)** ,难度为 **困难**。 |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +Tag : 「基环森林」、「内向基环树」、「拓扑排序」、「图」、「BFS」 |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +现有一个有向图,其中包含 `n` 个节点,节点编号从 `0` 到 `n - 1`。此外,该图还包含了 `n` 条有向边。 |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +给你一个下标从 `0` 开始的数组 `edges`,其中 `edges[i]` 表示存在一条从节点 `i` 到节点 `edges[i]` 的边。 |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +想象在图上发生以下过程: |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +你从节点 `x` 开始,通过边访问其他节点,直到你在 此过程 中再次访问到之前已经访问过的节点。 |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +返回数组 `answer` 作为答案,其中 `answer[i]` 表示如果从节点 `i` 开始执行该过程,你可以访问到的不同节点数。 |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +示例 1: |
| 20 | +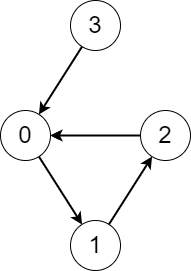 |
| 21 | +``` |
| 22 | +输入:edges = [1,2,0,0] |
| 23 | +
|
| 24 | +输出:[3,3,3,4] |
| 25 | +
|
| 26 | +解释:从每个节点开始执行该过程,记录如下: |
| 27 | +- 从节点 0 开始,访问节点 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0 。访问的不同节点数是 3 。 |
| 28 | +- 从节点 1 开始,访问节点 1 -> 2 -> 0 -> 1 。访问的不同节点数是 3 。 |
| 29 | +- 从节点 2 开始,访问节点 2 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 。访问的不同节点数是 3 。 |
| 30 | +- 从节点 3 开始,访问节点 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 0 。访问的不同节点数是 4 。 |
| 31 | +``` |
| 32 | +示例 2: |
| 33 | +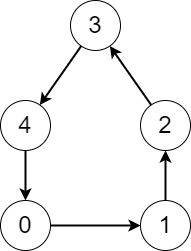 |
| 34 | +``` |
| 35 | +输入:edges = [1,2,3,4,0] |
| 36 | +
|
| 37 | +输出:[5,5,5,5,5] |
| 38 | +
|
| 39 | +解释:无论从哪个节点开始,在这个过程中,都可以访问到图中的每一个节点。 |
| 40 | +``` |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +提示: |
| 43 | +* $n = edges.length$ |
| 44 | +* $2 <= n <= 10^5$ |
| 45 | +* $0 <= edges[i] <= n - 1$ |
| 46 | +* $edges[i] != i$ |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +--- |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +### 内向基环森林 + 拓扑排序 |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +根据题意,共 `n` 个点,`n` 条边,利用 `edges`,将 `i` 向 `edges[i]` 连有向边,可知每个点有唯一的出边,因此这是一张可能包含多棵「内向基环树」的「基环森林」。 |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +基环树是指其具有 $n$ 个点 $n$ 条边的联通块,而「内向」是指树中任意节点有且只有一条出边,对应的「外向」是指树中任意节点有且只有一条入边。 |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +例如,左图内向,右图外向: |
| 57 | + |
| 58 | +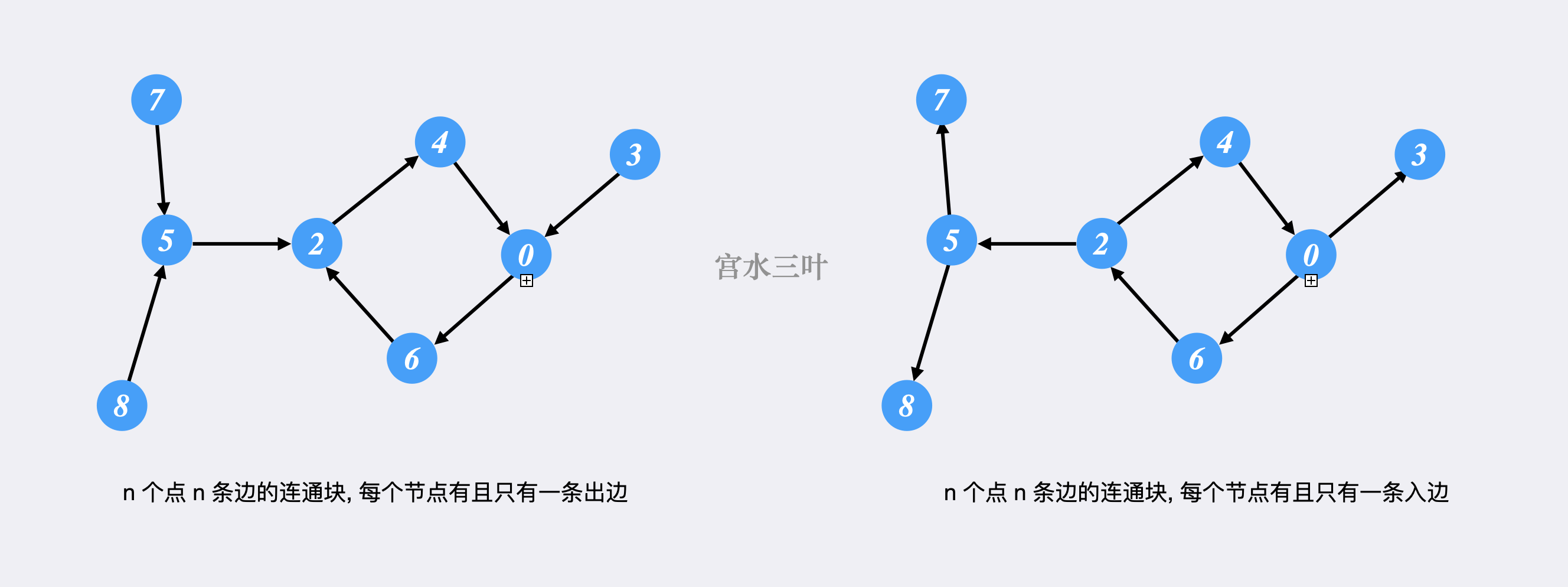 |
| 59 | + |
| 60 | +显然,可根据当前节点是否在“环内”进行分情况讨论: |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +* 对于「环内」节点来说,其答案为环节点个数; |
| 63 | +* 对于「环外」节点来说,直观感受应该是由环上节点转移而来。但由于本题给定的是「内向基环树」,因此我们需要对原图进行“反向”,然后从环内节点开始,进行 `BFS` ,从而更新其余非环节点答案。 |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +具体的,我们使用如下思路进行求解: |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +1. 创建大小为 `n` 的数组 `in`,进行入度统计; |
| 68 | +2. 根据入度进行「拓扑排序」,剩余满足 $in[i] \neq 0$ 的点,为「环内」的点。我们可处理出每个点所在环的大小,环的大小为这些点的答案。处理过程中收集这些「环内」的点(将来要从它们出发,更新其他「环外」节点) |
| 69 | +3. 对原图进行“反向”,从收集好的「环内」点进行出发,运用 `BFS` 得出剩余点答案。 |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +Java 代码: |
| 72 | +```Java |
| 73 | +class Solution { |
| 74 | + int N = 200010, M = N, idx = 0; |
| 75 | + int[] he = new int[N], e = new int[M], ne = new int[M]; |
| 76 | + void add(int a, int b) { |
| 77 | + e[idx] = b; |
| 78 | + ne[idx] = he[a]; |
| 79 | + he[a] = idx++; |
| 80 | + } |
| 81 | + public int[] countVisitedNodes(List<Integer> edges) { |
| 82 | + int n = edges.size(); |
| 83 | + int[] in = new int[n], ans = new int[n]; |
| 84 | + for (int x : edges) in[x]++; |
| 85 | + Deque<Integer> d = new ArrayDeque<>(); |
| 86 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 87 | + if (in[i] == 0) d.addLast(i); |
| 88 | + } |
| 89 | + while (!d.isEmpty()) { |
| 90 | + int t = edges.get(d.pollFirst()); |
| 91 | + if (--in[t] == 0) d.addLast(t); |
| 92 | + } |
| 93 | + // 处理环上的 |
| 94 | + Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); |
| 95 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 96 | + if (in[i] == 0) continue; |
| 97 | + List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); |
| 98 | + list.add(i); |
| 99 | + int j = edges.get(i), val = 1; |
| 100 | + while (j != i) { |
| 101 | + list.add(j); |
| 102 | + j = edges.get(j); |
| 103 | + val++; |
| 104 | + } |
| 105 | + for (int x : list) { |
| 106 | + set.add(x); |
| 107 | + in[x] = 0; |
| 108 | + ans[x] = val; |
| 109 | + } |
| 110 | + } |
| 111 | + // 建立反向图, 处理非环上的, 从环内点出发进行往外更新 |
| 112 | + Arrays.fill(he, -1); |
| 113 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) add(edges.get(i), i); |
| 114 | + for (int u : set) { |
| 115 | + int val = ans[u]; |
| 116 | + Deque<Integer> de = new ArrayDeque<>(); |
| 117 | + de.addLast(u); |
| 118 | + while (!de.isEmpty()) { |
| 119 | + int sz = de.size(); |
| 120 | + while (sz-- > 0) { |
| 121 | + int t = de.pollFirst(); |
| 122 | + ans[t] = val; |
| 123 | + for (int i = he[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) { |
| 124 | + int j = e[i]; |
| 125 | + if (ans[j] != 0) continue; |
| 126 | + de.addLast(j); |
| 127 | + } |
| 128 | + } |
| 129 | + val++; |
| 130 | + } |
| 131 | + } |
| 132 | + return ans; |
| 133 | + } |
| 134 | +} |
| 135 | +``` |
| 136 | +C++ 代码: |
| 137 | +```C++ |
| 138 | +class Solution { |
| 139 | +public: |
| 140 | + int he[200010], e[200010], ne[200010], idx; |
| 141 | + void add(int a, int b) { |
| 142 | + e[idx] = b; |
| 143 | + ne[idx] = he[a]; |
| 144 | + he[a] = idx++; |
| 145 | + } |
| 146 | + vector<int> countVisitedNodes(vector<int>& edges) { |
| 147 | + int n = edges.size(); |
| 148 | + vector<int> in(n, 0), ans(n, 0); |
| 149 | + for (int x : edges) in[x]++; |
| 150 | + queue<int> d; |
| 151 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 152 | + if (in[i] == 0) d.push(i); |
| 153 | + } |
| 154 | + while (!d.empty()) { |
| 155 | + int t = edges[d.front()]; |
| 156 | + d.pop(); |
| 157 | + if (--in[t] == 0) d.push(t); |
| 158 | + } |
| 159 | + set<int> s; |
| 160 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 161 | + if (in[i] == 0) continue; |
| 162 | + vector<int> list; |
| 163 | + list.push_back(i); |
| 164 | + int j = edges[i], val = 1; |
| 165 | + while (j != i) { |
| 166 | + list.push_back(j); |
| 167 | + j = edges[j]; |
| 168 | + val++; |
| 169 | + } |
| 170 | + for (int x : list) { |
| 171 | + s.insert(x); |
| 172 | + in[x] = 0; |
| 173 | + ans[x] = val; |
| 174 | + } |
| 175 | + } |
| 176 | + memset(he, -1, sizeof(he)); |
| 177 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) add(edges[i], i); |
| 178 | + for (int u : s) { |
| 179 | + int val = ans[u]; |
| 180 | + queue<int> de; |
| 181 | + de.push(u); |
| 182 | + while (!de.empty()) { |
| 183 | + int sz = de.size(); |
| 184 | + while (sz-- > 0) { |
| 185 | + int t = de.front(); |
| 186 | + de.pop(); |
| 187 | + ans[t] = val; |
| 188 | + for (int i = he[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) { |
| 189 | + int j = e[i]; |
| 190 | + if (ans[j] != 0) continue; |
| 191 | + de.push(j); |
| 192 | + } |
| 193 | + } |
| 194 | + val++; |
| 195 | + } |
| 196 | + } |
| 197 | + return ans; |
| 198 | + } |
| 199 | +}; |
| 200 | +``` |
| 201 | +* 时间复杂度:统计入度复杂度为 $O(n)$;拓扑排序复杂度为 $O(n)$;统计「环内」节点答案复杂度为 $O(n)$;统计「环外」答案复杂度为 $O(n)$。整体复杂度为 $O(n)$ |
| 202 | +* 空间复杂度:$O(n)$ |
| 203 | +
|
| 204 | +--- |
| 205 | +
|
| 206 | +### 最后 |
| 207 | +
|
| 208 | +这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 `No.2876` 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。 |
| 209 | +
|
| 210 | +在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。 |
| 211 | +
|
| 212 | +为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。 |
| 213 | +
|
| 214 | +在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。 |
| 215 | +
|
0 commit comments